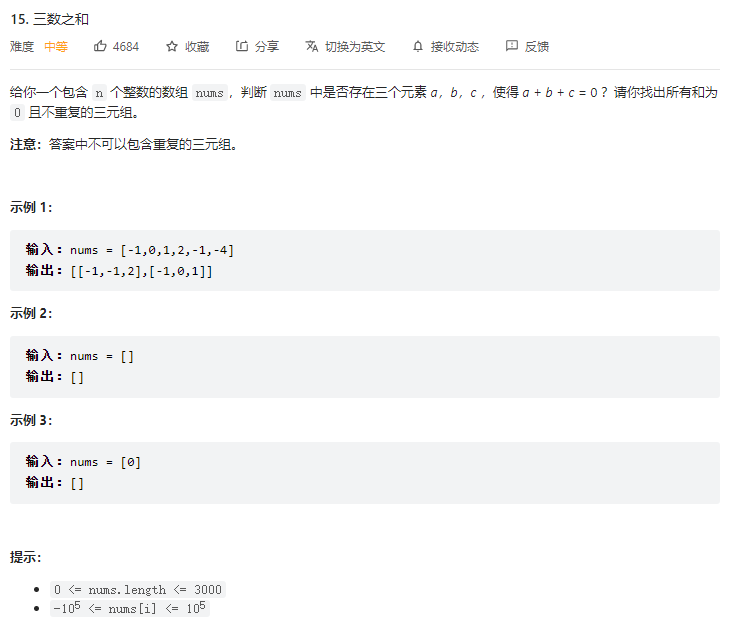
【算法题目】【DFS】Python 三数之和 DFS+剪枝 排序 + 双指针
目录
DFS+剪枝:直接超时:
python展开代码class Solution:
def threeSum(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
def dfs(start, sol: List):
# print(sol)
if start > n: # 结束条件,
return
if len(sol) >= 3:
if sum(sol) == 0:
res.append(sol[:])
return
for i in range(start, len(nums)):
if i > start and nums[i] == nums[i - 1]: # 为了排除相同结果
continue
sol.append(nums[i])
dfs(i + 1, sol)
sol.pop()
nums.sort()
n = len(nums)
res = []
dfs(0, [])
return res
排序 + 双指针
双指针双向移动也能减少计算,拿到结果就能拜拜进行下一次,不像DFS没有太考虑数据的有序性,在DFS中的排序仅仅剪枝用了一下。
python展开代码class Solution:
def threeSum(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
n = len(nums)
nums.sort()
ans = list()
# 枚举 a
for first in range(n):
# 需要和上一次枚举的数不相同
if first > 0 and nums[first] == nums[first - 1]:
continue
# c 对应的指针初始指向数组的最右端
third = n - 1
target = -nums[first]
# 枚举 b
for second in range(first + 1, n):
# 需要和上一次枚举的数不相同
if second > first + 1 and nums[second] == nums[second - 1]:
continue
# 需要保证 b 的指针在 c 的指针的左侧
while second < third and nums[second] + nums[third] > target:
third -= 1
# 如果指针重合,随着 b 后续的增加
# 就不会有满足 a+b+c=0 并且 b<c 的 c 了,可以退出循环
if second == third: # 指针位置性
break
if nums[second] + nums[third] == target:
ans.append([nums[first], nums[second], nums[third]])
return ans
如果对你有用的话,可以打赏哦
打赏


本文作者:Dong
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC。本作品采用《知识共享署名-非商业性使用 4.0 国际许可协议》进行许可。您可以在非商业用途下自由转载和修改,但必须注明出处并提供原作者链接。 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录